Blink Uploads Succcessfully on Esp but Does Not Work
Internet has reached nigh every pocket through smart phones, it is estimated that about iii.ii billion people apply cyberspace simply surprisingly almost eight.4 billion devices apply net. That is electronics devices are continued to internet more than twice of the population who use cyberspace and information technology is making the things effectually us smarter every mean solar day. The major reason is the boom of Internet of things which is commonly known every bit IOT, it is also estimated that past the cease of 2020 we volition have 20.4 billion devices connected to the internet. So it's time to ready and ascent up our sleeves to work with IOT projects if nosotros want to keep up with this evolution, lucky for us the open up source platforms similar Arduino and Espressif Systems has made things a lot easy for usa.
Espressif Systems launched the ESP8266-01 long back which opened doors to many hobbyists to go into the world of IOT, since then the community has been developing strongly and many products has hit the market. Now the launch of ESP32 Espressif has taken things to a new level. This tiny cheap 8$ module is a dual core 32-bit CPU with built in Wi-Fi and dual-mode Bluetooth with sufficient amount of 30 I/O pins for all basic electronics projects. All these features are very piece of cake to use, since information technology can be programmed directly from the Arduino IDE. Exciting enough... So let's dig deep to get started with the ESP32.
Materials Required:
- ESP32 Module
- Arduino IDE
- Programming cablevision (micro USB cable)
- The soul rock from MCU (just kidding)
Hardware Information of ESP32:
Permit's take a look at the ESP32 module. It is slightly bigger than the ESP8266-01 module and is breadboard friendly since most of the pin headers are broken out as I/O pins facing each other which is a great thing. Let's intermission the board into pocket-size parts to know the purpose of each segment
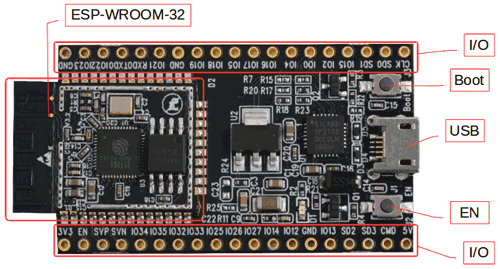
Equally you can come across the eye of the module is the ESP-WROOM-32 which is a 32-scrap microprocessor. It also has a couple of buttons and LEDs which are explained below.
Micro-USB jack: The micro USB jack is used to connect the ESP32 to our computer through a USB cable. It is used to program the ESP module too as can be used for serial debugging as it supports serial communication
EN Button: The EN button is the reset push of the ESP module. Pressing this button will reset the code running on the ESP module
Boot Push button: This push is used to upload the Program from Arduino to the ESP module. It has to be pressed later clicking on the upload icon on the Arduino IDE. When the Kicking push is pressed along with the EN button, ESP enters into firmware uploading mode. Do not play with this fashion unless you lot know what you are doing.
Cherry-red LED: The Cherry LED on the board is used to bespeak the power supply. It glows red when the board is powered.
Blue LED: The Blue LED on the board is connected to the GPIO pin. It can be turned on or off through programming. In some Chinese cloned boards like mine, this led might also be in red colour.
I/O pins: This is where major evolution has taken identify. Different ESP8266, on ESP32 we tin admission all the I/O pin of the module through the interruption-out pins. These pins are capable of Digital Read/Write, Analog Read/Write, PWM, IIC, SPI, DAC and much more. Nosotros will get more into that afterward. But if you are interested you lot can learn through the pin description at ESP32 Datasheet.
ESP-WROOM-32: This is the heart of the ESP32 module. It is a 32-fleck microprocessor developed past Espressif systems. If you are more of a technical person y'all can read through the ESP-WROOM-32 Datasheet. I have also listed few important parameters beneath.
| ESP32 | |
| Specification | Value |
| Number of cores | two |
| Architecture | 32 bit |
| CPU Frequency | |
| Wi-Fi | Yep |
| Bluetooth | Yep |
| RAM | 512 KB |
| Wink | 16 MB |
| GPIO Pins | 36 |
| Communication Protocols | SPI, IIC, I2S, UART, CAN |
| ADC channels | 18 channels |
| ADC Resolution | 12-chip |
| DAC channels | 2 |
| DAC Resolution | eight-bit |
For at present this is all the information that nosotros need to know about the hardware. We volition cover more in depth every bit we move with dissimilar projects using the ESP32.
Programming the ESP32
Every bit mentioned earlier in this tutorial we are going to program the ESP32 using the Arduino IDE since information technology has a potent community support. But you lot can besides program the ESP32 using other software by the ESP Toolchain.
Besides, this tutorial will only explain on getting started with the windows platform. If y'all are from other platforms follow the links below
- Instructions for Mac
- Instructions for Debian/Ubuntu Linux
- Instructions for Fedora
- Instructions for openSUSE
Preparing your Arduino IDE:
Footstep 1: Now, let's get started. The starting time step would exist to download and install the Arduino IDE. This can be done easily by following the link https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software and downloading the IDE for free. If y'all already have one make sure it is of the latest version.
Footstep 2: Adjacent proceed to this link to download GIT, and a download will begin automatically named "Git-2.16.ii". Await for the downloading to complete.
STEP 3: In one case the download is complete, open the exe file to install GIT on your computer. Simply click on Next for all the options without changing anything to proceed with the installation.
STEP 4: Search for the name "GIT GUI" to observe the 1 that we but installed. Do not open GIT bash. By default GIT GUI will be installed on C drive under the Plan files directory
Footstep 5: Launch the GIT GUI application. So select "Clone exiting repository".
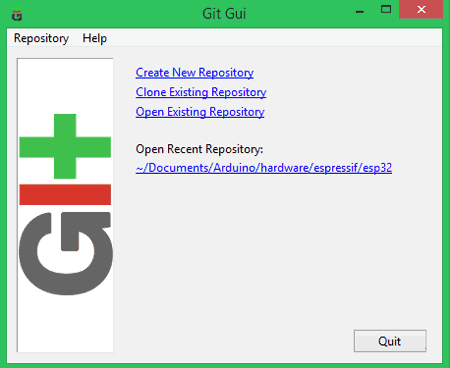
STEP 6: The following window will announced in which you should do the following.
Under Source Location paste: https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32.git
Under Target Directory Paste: [ARDUINO_SKETCHBOOK_DIR]/hardware/espressif/esp32
[ARDUINO_SKETCHBOOK_DIR] can exist establish by clicking on File -> Preferences on the Arduino IDE
Mine is C:/Users/Aswinth/Documents/Arduino, so my target directory will be C:/Users/Aswinth/Documents/Arduino/hardware/Espressif/esp32. Once pasted my screen looked liked as shown below
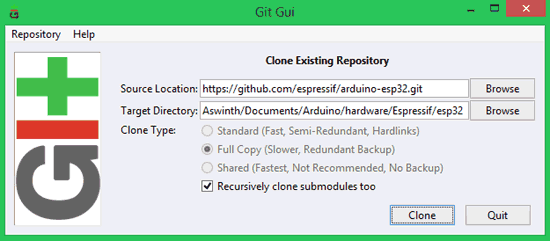
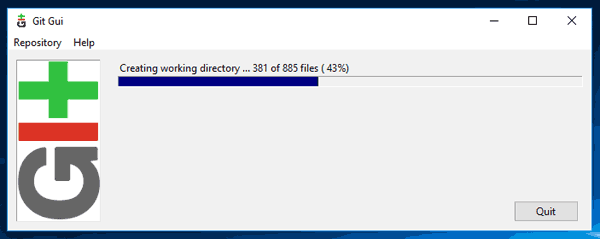
STEP seven: Subsequently ensuring the correct location paths, click on clone and you will get the following screen.
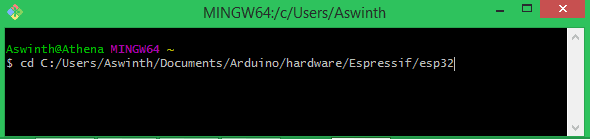
STEP 8: Now again search for "Git Bash" and open information technology. Y'all will get the post-obit window.

Stride 9: Now type "cd" so paste your Target directory once again here. Mine looked like this below after pasting. Then hit enter.
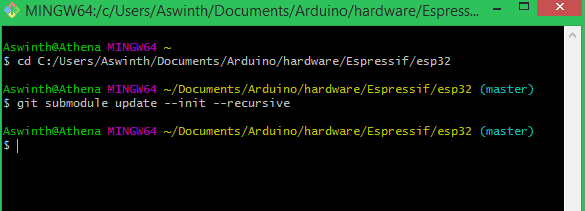
Footstep ten: Now paste git submodule update --init –recursive and hit enter to get the following screen.
STEP 11: Now open "[ARDUINO_SKETCHBOOK_DIR]/hardware/espressif/esp32/tools" so double click on the file get.exe. Look for the process to cease. In one case completed y'all should see the following files on the directory
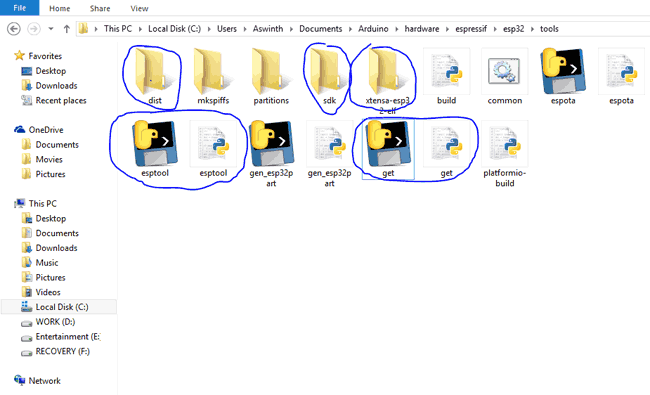
That is it now our Arduino IDE is prepared to work with ESP32. Let'south go ahead and cheque if information technology is working.
Programming ESP32 with Arduino IDE:
STEP 1: Connect your ESP32 lath to your computer through the micro-USB cable. Make sure the red LED goes loftier on the module to ensure power supply.
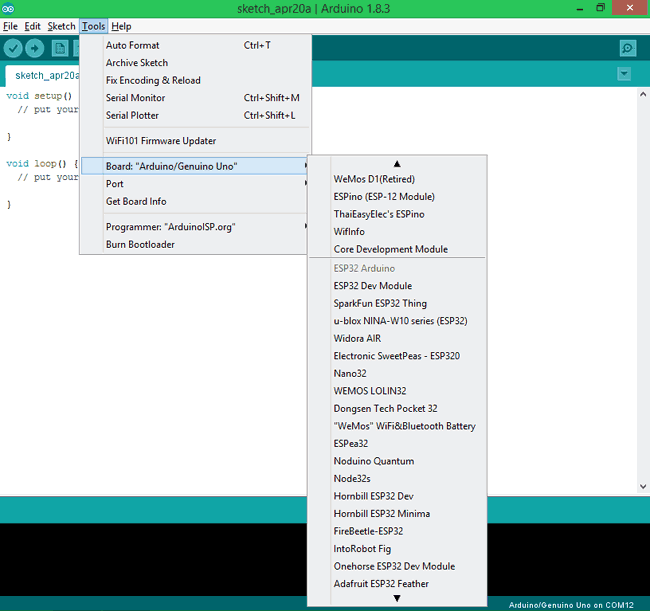
STEP2: Get-go the Arduino IDE and navigate to Tools -> Boards and select ESP32Dev board as shown beneath
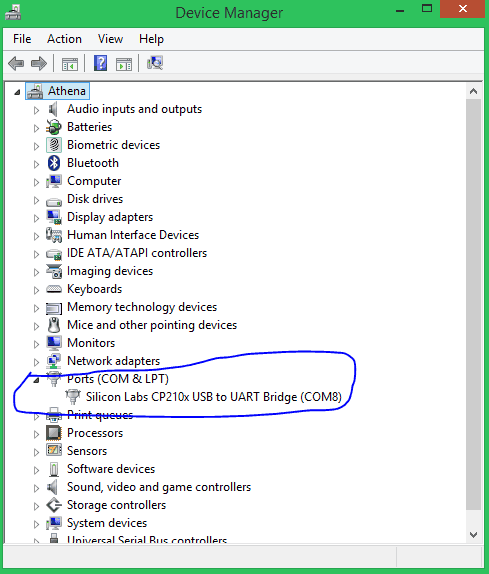
STEP 3: Open up device manager and bank check to which com port your ESP32 is continued to. Mine is connected to COM 8 as shown below
Pace four: Go back to Arduino IDE and under Tools -> Port select the Port to which your ESP is continued to. In one case selected you should run across something like this on the bottom left corner of the IDE.
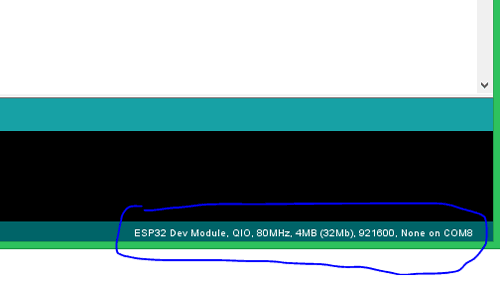
Pace 5: Let's upload the Blink Program, to cheque if we are able to program our ESP32 module. This programme should blink the LED at an interval of 1 second.
int LED_BUILTIN = 2; void setup() { pinMode (LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT); } void loop() { digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); delay(1000); digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, Depression); delay(m); } The programme is very like to the Arduino blink code hence I am not explain them in particular. Merely ane change is that, here in ESP32 the LED on board is connected to pin number 2, while for Arduino information technology will be connected to pin number 13.
STEP 6: To upload the code, just click on upload and you lot should see the Arduino console displaying the following if everything works every bit expected.
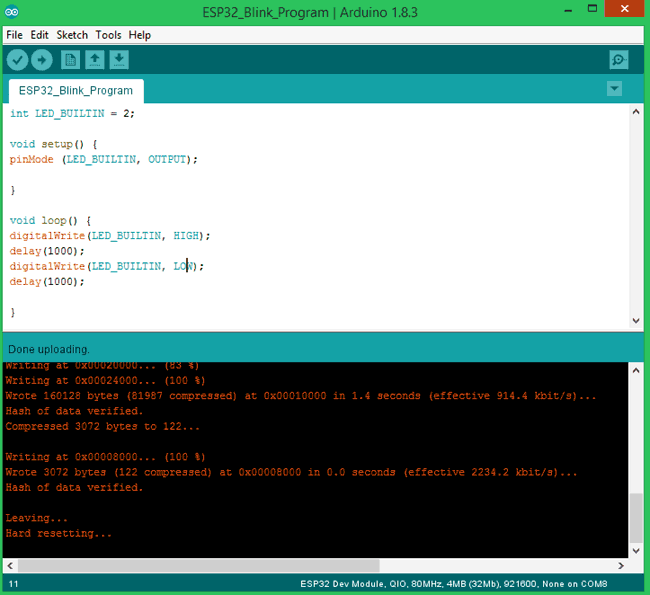
Note: For some modules, you might have to agree the Boot button during uploading to avoid mistake.
That is it nosotros have successfully uploaded out start code to our ESP32 lath. My module with its LED blinking is shown below
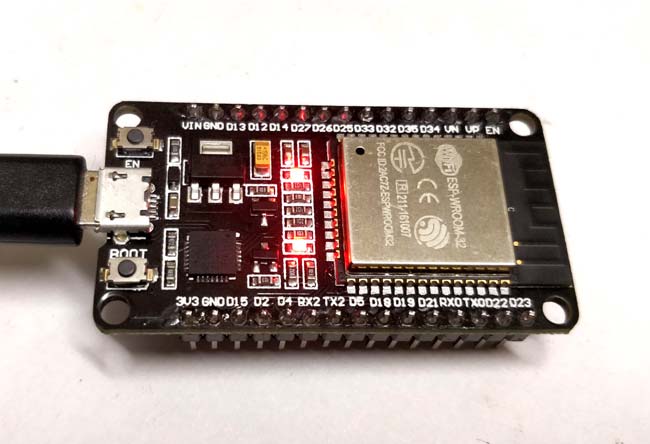

Yous can go ahead and try the other instance programs which are available at File -> Example -> ESP32 to work with other functionalities of the ESP32. If you have had whatsoever problem in getting this work, feel gratis to mail service the query on the comment sections below. You lot can also utilize the Forum for getting technical help.
Code
int LED_BUILTIN = 2;
void setup() {
pinMode (LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, Low);
filibuster(yard);
}
Source: https://circuitdigest.com/microcontroller-projects/getting-started-with-esp32-with-arduino-ide
0 Response to "Blink Uploads Succcessfully on Esp but Does Not Work"
Post a Comment